Many developers sometimes confuse which is better to parse the XML document. Ofcourse myself also got doubt which parser I can use for this situation. Since I have read about DOM and SAX very long back. Just refreshing it again
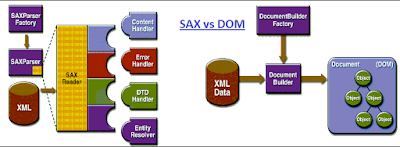
DOM (Document Object Model) Parser:
- Tree model parser(Object based) (Tree of nodes).
- DOM loads the file into the memory and then parse the file.
- Has memory constraints since it loads the whole XML file before parsing.
- DOM is read and write (can insert or delete the node).
- If the XML content is small then prefer DOM parser.
- Backward and forward search is possible for searching the tags and evaluation of the information inside the tags. So this gives the ease of navigation.
- Slower at run time.
- Event based parser (Sequence of events). Event based means..don't be confused with word "event". Here event means. (e.g. <something>), then it triggers the tagStarted event (actual name of event might differ). Similarly when the end of the tag is met while parsing (</something>), it triggers tagEnded. Using a SAX parser implies you need to handle these events and make sense of the data returned with each event.
- SAX parses the file at it reads i.e. Parses node by node.
- No memory constraints as it does not store the XML content in the memory.
- SAX is read only i.e. can’t insert or delete the node.
- Use SAX parser when memory content is large.
- SAX reads the XML file from top to bottom and backward navigation is not possible.
- Faster at run time.
Comments
Post a Comment