Recently, I started working on Ubuntu OS 14.04. I feel Ubuntu is much simpler than what I thought earlier. Lets leave about Ubuntu, I want to blog more about Ubuntu OS afterwards. Here I want to brief about how to install Tomcat webserver on Ubuntu. Apache Tomcat is an open source webserver where we can deploy java applications.
Go to terminal window on Ubuntu and login as a root user.
1. Install Java First:
Go to terminal window on Ubuntu and login as a root user.
1. Install Java First:
- Before installing Tomcat server, it is better to install Java. Run the following command on terminal window to check Java is already installed.
- If it returns "The program 'java' can be found in the following packages:" the Java is not installed on Ubuntu. To install Java, just run the below command. After this we have to add Java to environment variables in .bashrc. We will add both Java and Tomcat after the installation of Tomcat webserver.
apt-get install default-jdk
2. Install Tomcat Webserver
There are two ways to install Tomcat in Ubuntu.
2. Install Tomcat Webserver
There are two ways to install Tomcat in Ubuntu.
- The first method is simply run the below command on terminal window.
- The second method is installing tomcat from binaries. Click on Apache Tomcat7 Download site. The latest version of Tomcat is 7.0.63 as on July 2015. Just right click on tar.gz under Core: and copy the URL link as shown below.
- Now run the following command with copied link terminal window. I suggest phrase the command in notepad and copy on command prompt and enter. So that we can make sure that we don't miss any letter in URL while pasting it on terminal window. Otherwise you can do as your comfort.
- Decompress the file after downloading with below command.
tar xvzf apache-tomcat-7.0.63.tar.gz
- Move the tomcat to the right location with below command.
mv apache-tomcat-7.0.53 /opt/tomcat
Now we have to add Java and Tomcat to environment variables of Ubuntu OS. Just open the .bashrc with vim editor. You can find some tutorials online on how to use vim editor on Ubuntu.
- Run the following command.
- Add the below two lines to the end of the .bashrc file and save then exit.
export CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat
- To ensure the changes are effected run the following command.
. ~/.bashrc
- Run the below command to start the tomcat.
- If you get following result, then we have done proper installation of tomcat and Java.
Using CATALINA_HOME: /opt/tomcat
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /opt/tomcat/temp
Using JRE_HOME: /usr/lib/jvm/default-java
Using CLASSPATH: /opt/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar:/opt/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
Tomcat started.
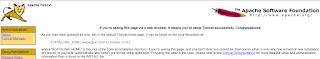
- We can verify the Tomcat is running successfully or not. Just open the browser and type http://localhost:8080/ or http://127.0.0.1:8080/ and enter. Then you will see the screen as shown in below image.

Comments
Post a Comment